Ask & Prompt Dataset
Abstract
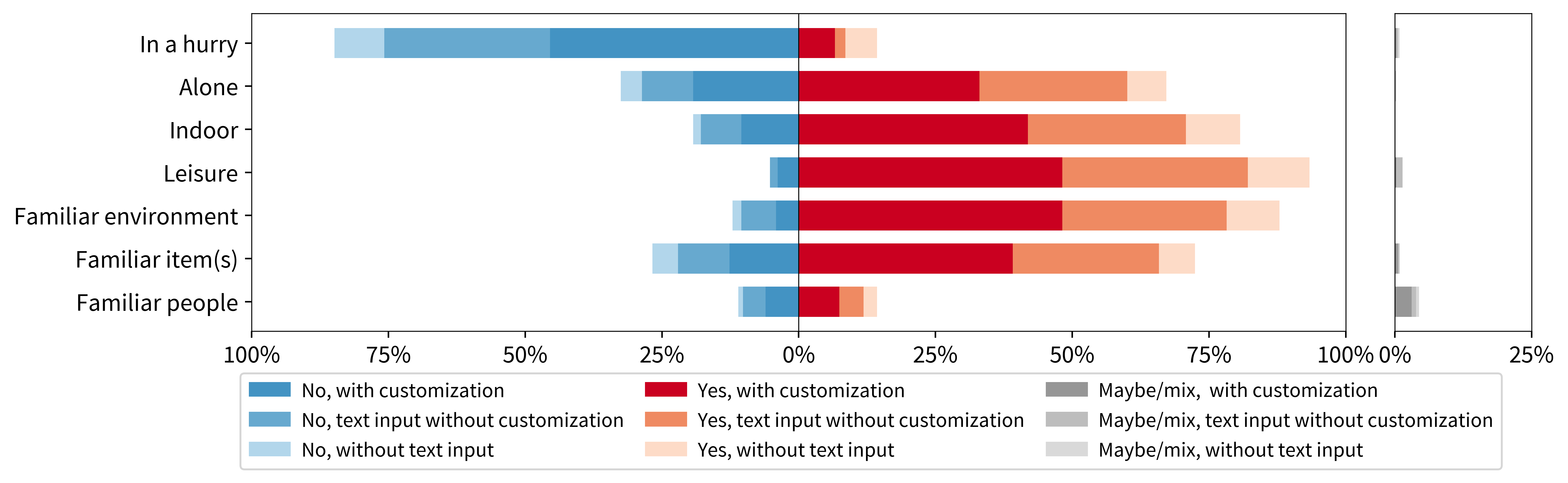
While prompting and steering techniques have been actively developed in general-purpose generative AI, there are not many resources for assistive visual question answering (VQA) systems and blind users; interfaces follow rigid patterns of interactions with limited opportunities for customization. We invite 11 blind users to customize their interactions with a conversational VQA system. Drawing on 418 interactions, reflections, and post-study interviews, we analyze prompting-based techniques participants adopted, including those introduced in the study and those developed independently in real-world settings. VQA interactions were often lengthy: participants averaged 3 turns, sometimes up to 21, with input text typically tenfold shorter than the responses they heard. Even assistive applications built on state-of-the-art LLMs often lacked verbosity controls, relied on inaccessible image framing, and offered no camera guidance. We show how customization techniques such as prompt engineering can help participants work around these limitations. Alongside a new publicly available dataset, we offer insights for interaction design at both query and system levels
JSON Data Structure
Two json files for each participant (in_lab_interactions.json and diary_interactions.json) share the same structure. Below is the structure of the JSON data.
{"interaction_link": [
{
"interaction_idx": ,
"turn": ,
"text_usr": ,
"text_ai": ,
"image_url": ,
"local_image_path":
},...]
}...